
by jhwildlife | Mar 7, 2017 | Blog, Nature Mapping Jackson Hole

Earle Layser spots moose tracks in West Jackson
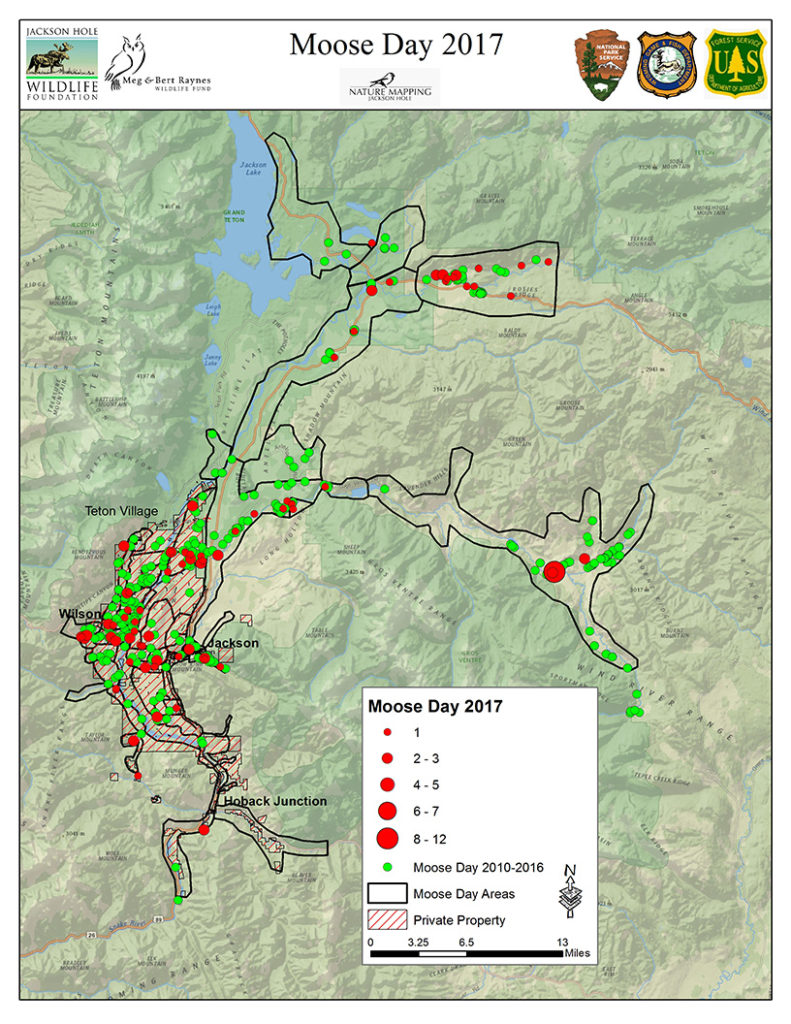
Moose Day 2017 set a record for community participation and for the number of moose counted. We extend our thanks to the Nature Mappers and new recruits as well as, biologists from Wyoming Game & Fish Department, Grand Teton National Park and U.S. Forest Service. All volunteered their time from 7 a.m. to 12 noon on Saturday, February 25.
This year, a total of 33 teams, comprising 83 volunteers counted 166 moose, contributing over 290 hours time.
This exceeds our previous record of 124 moose in 2011, and the 99 moose seen last year. Volunteer numbers are well over our 65 person average. In 2016, we had 73 participants helping with the count. This was our 9th annual Moose Day.
Volunteers snowmobiled, snowshoed, drove, walked and most of all, climbed up snow banks to scout moose! Many were rewarded by seeing moose — in some cases many! Successful surveyors often had local tips or tracked fresh moose sign to find hidden individuals. In other cases, neighborhood teams were disappointed to not see the moose that was “there yesterday” and saw no moose at all. However, zero (0) moose is important data as well. And, it is clear that moose move!
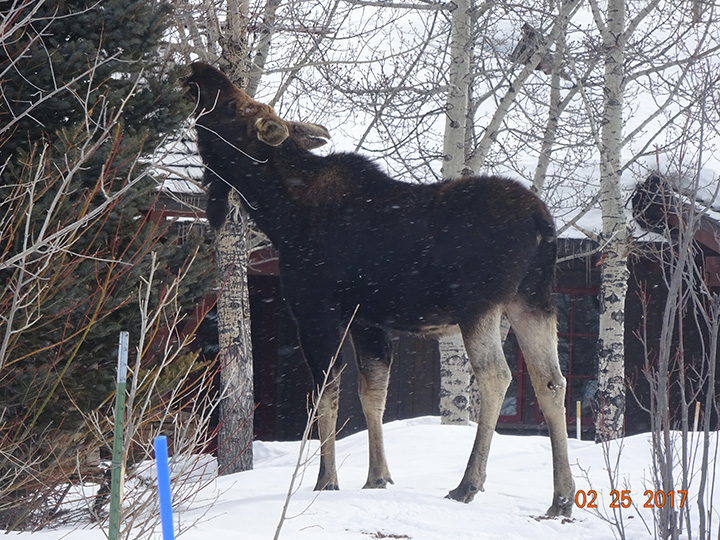

A moose feeding by Randy Reedy
Where were the moose this year? It appears they were attracted to low-lying willow wetlands, such as Buffalo Fork Valley, along the Gros Ventre River and in Wilson. For instance, Kerry Murphy and his U.S. Forest Service team were able to survey the Gros Ventre all the way east to Darwin Ranch. Along this route, often with extensive willow stands, they surveyed 57 moose! Much closer to civilization, moose were seen browsing on exotic shrubs in Jackson or loafing in the shelter of buildings. In a few spots, moose were even congregating close to horses.
Where were moose missing? Often in areas of extremely deep snow, such as the northern stretches of Grand Teton National Park and at the base of the mountains along Fish and Fall Creek Roads. Other wide open areas had little browse for the amount of effort it would take to reach it. Fortunately, most reports indicate moose were in good condition.
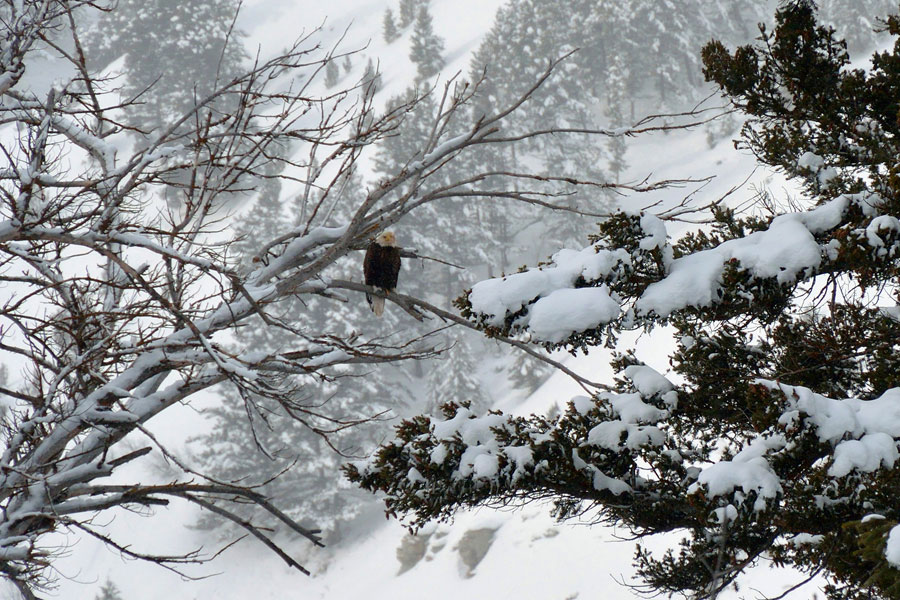

Other critters like Bald Eagles were mapped, too. Photo by Alice Cornell
Whether Nature Mappers saw moose or not, they reported a good time. Many observed (and mapped) other critters as well: wolf, coyote, Trumpeter Swans, otter, beaver, Bald Eagles, elk, Red Crossbills, a dipper and other birds. Teams of friends and strangers enjoyed each other’s company for the morning, and over 30 volunteers showed up at E.Leaven for lunch to share their stories. Moose Day is very much a community event!
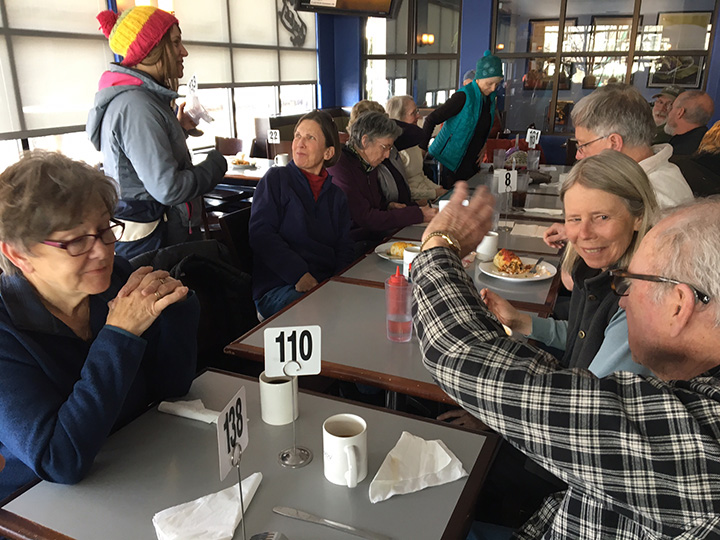

30 moose mappers recounting the morning’s count at E. Leaven. Photo by Frances Clark

Moose munching by Mary Lohuis
Moose Day is important because we survey moose on private lands, where public-land biologists rarely go. We thank the Snake River Ranch, Snake River Sporting Club, Jackson Holf Golf & Tennis, and Trail Creek Ranch as well as, homeowner associations and individuals for granting permission for us to survey their private property. Without their support we would not have counted so many moose!
Next, Paul Hood and Aly Courtemanch will analyze the data and produce a formal 2017 Moose Day report. This report will enable biologists to determine trends in moose populations and planners to understand where moose roam and rest.
Again, many many thanks to the Nature Mapping Jackson Hole community for caring about our Teton County moose!
Frances Clark
Moose Day Coordinator
Note: Moose By The River photo by Alice Cornell

by jhwildlife | Feb 27, 2017 | Blog, Nature Mapping Jackson Hole
by Susan Marsh
When Nature Mapping Jackson Hole began in 2009, Project Backyard (PBY) was born. It was the first systematic observation protocol developed for Nature Mapping Jackson Hole, meant to augment the casual observations that people recorded while driving or wandering along the mountain trails. What’s the difference between PBY and casual observations, and why does it matter?
A good example may be taken from our first attempt at counting moose on a single day for Nature Mapping Jackson Hole, prior to the start of the organized Moose Day, for which observers are assigned specific areas. On that first count we had lots of observations, but many of them turned out to be the same dozen moose in the Antelope Flats area. It became clear that casual observations could only give so much accuracy on a single day.
What was the best way to achieve a more systematic approach that would be easy for people to work with? Asking homeowners to record what they saw from their backyards seemed like the answer.
Participants in PBY make weekly observations, recording the maximum number of each species seen during a single week. No need to use a GPS unit – anyone participating in the project enters the coordinates for their location once, and they come up automatically each time. You can do it less frequently than weekly, and you don’t have to sit watching the bird feeder all day – just note what you see.

The response has been remarkable. Over 19,140 observations have been made in Project Backyard. These observations are particularly valuable as they provide information about the wildlife living in, or moving through, our neighborhoods and agricultural lands. While the federal agencies and Wyoming Game & Fish Department conduct wildlife counts on public land, they are often geared toward particular species, such as the classification count each February on the National Elk Refuge. Private lands are not included in agency counts since access is not always granted. But if you live there, you can provide valuable insights. It is through private citizen observations that we know about where small elk herds are moving as they increasingly stay the winter in the Wilson area and elsewhere on the valley floor – especially in this high-snow year. It is through citizen observations that we know the winter of 2016-2017 has been a low year for many species of songbirds that are often seen in higher numbers at feeders.
We collect this information not just for our edification. Nature Mapping Jackson Hole receives requests from the county, environmental consulting companies, researchers, non-governmental organizations and land developers, asking for information about what wildlife species might be affected by upcoming plans. Any data that a private firm or individual receives also go to the Teton County Planning & Development Department. Our data help make good decisions for wildlife in the valley.

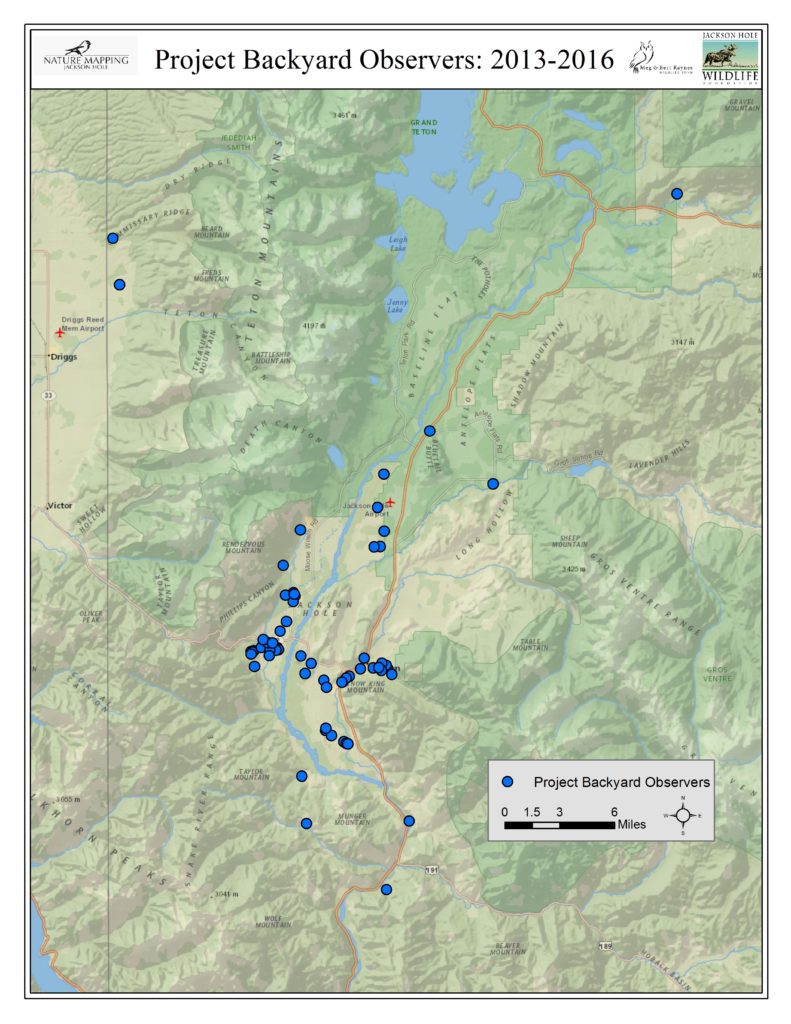
Some PBY observers have been providing information since the inception of the project. Others are welcome additions to the group, adding data from new locations that help give us a broader picture of Teton County wildlife. Many PBY observers are located in a few places — unsurprisingly, those areas where people live: Jackson, Wilson, Rafter J and along WY 22 and HWY 390. Others are located in Alta, Buffalo Valley and scattered from Munger Mountain to Blacktail Butte. It would be wonderful to fill some gaps where observations are not being made, including Moran, Spring Gulch and both Gros Ventre Buttes, the south end of the county, Hoback Junction, Kelly and the Shadow Mountain area. Populations are sparse in some of these spots, so there aren’t many backyards from which to observe. But slowly, we are building a valuable database using citizen science, thanks to the dedication of many people who care about the future of wildlife.
Project Backyard Observers 2013 – 2016:

by jhwildlife | Dec 14, 2016 | Blog, Nature Mapping Jackson Hole
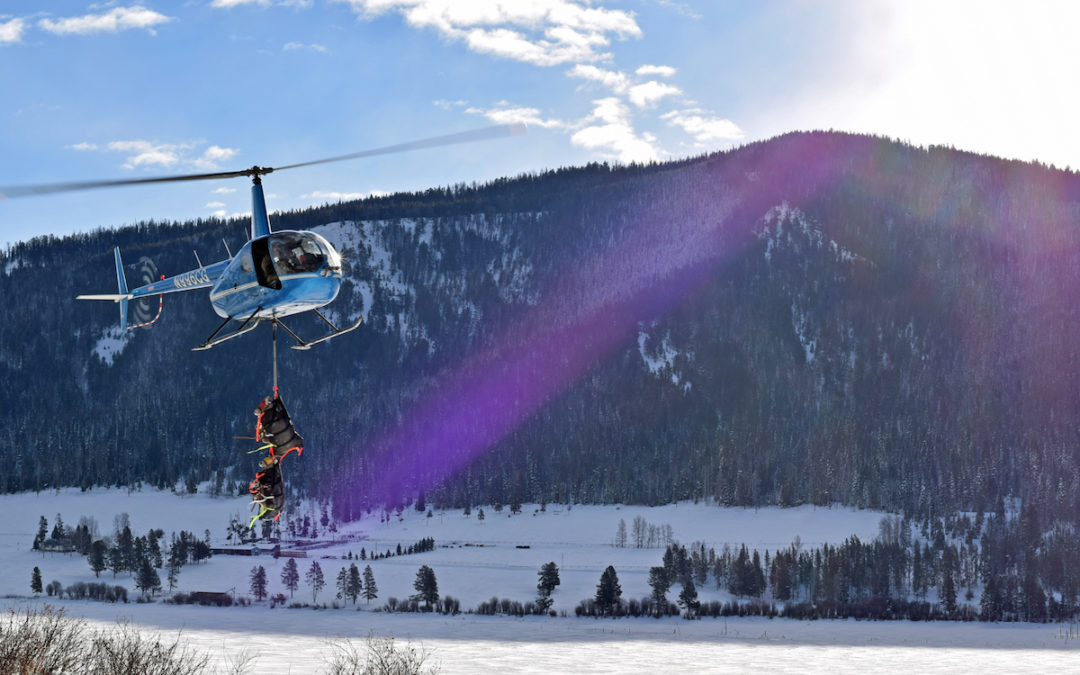
One of the perks of working for the Jackson Hole Wildlife Foundation is that occasionally you get invited by local scientists to do really, really cool stuff! Case in point, this past weekend staff traveled into the Gros Ventre Range with a crew of researchers to briefly capture, study and release bighorn sheep. Witnessing a small helicopter carrying blindfolded, restrained sheep at one or two at a time is very cool! This might sound alarming to some, that sheep would be transported from location to location via helicopter, but be assured that the animals are caught in the shortest possible time, with the least amount of stress. Furthermore, the purpose for this “trip of a lifetime” is to conduct science that will ensure the long-term survival of this iconic species of the American West.
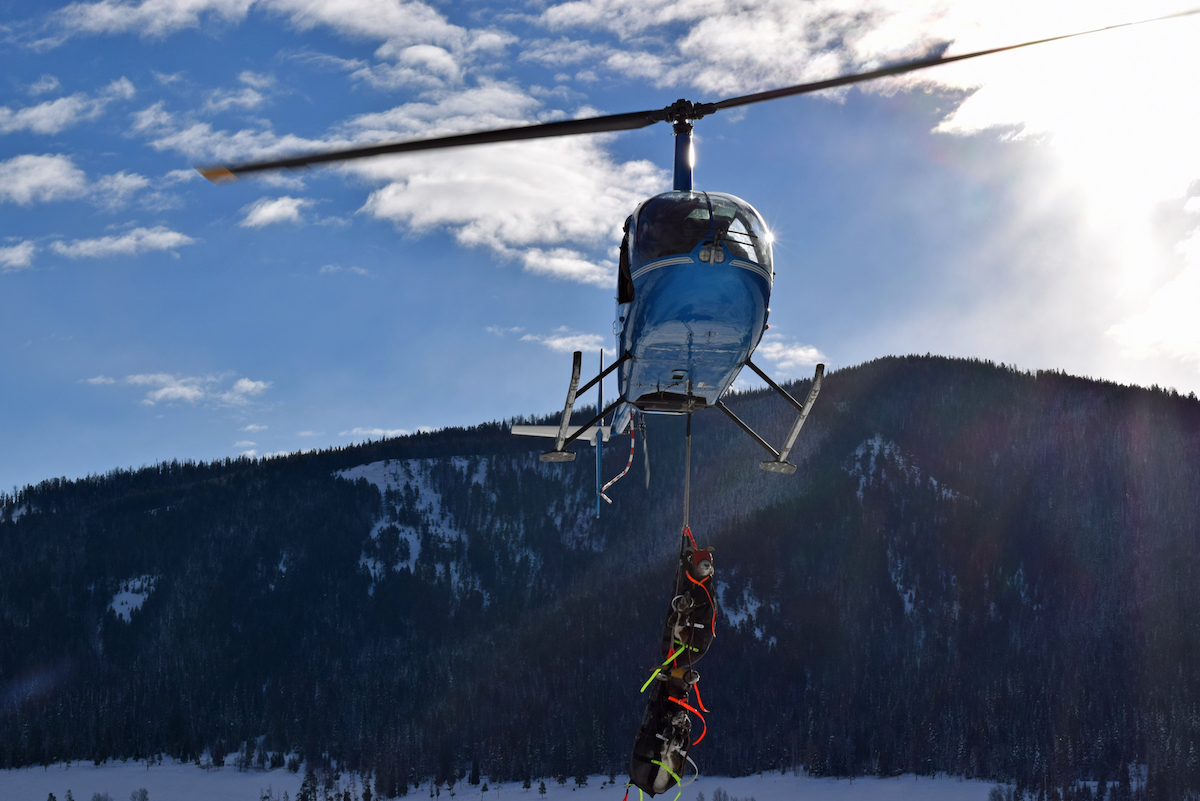

The helicopter brings in two bighorn sheep for a gentle landing.
The Wyoming Game and Fish Department (WGFD) is continuing its multi-year research project on bighorn sheep in the Jackson Region. On December 10 and 11, 2016, 10 female bighorn sheep (previously fitted with radio collars) were captured for disease testing in an effort to learn more about their survival and migration patterns. Samples were collected to test for respiratory pathogens that can cause pneumonia. In addition, researchers from Dr. Kevin Monteith’s lab at Wyoming Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit at the University of Wyoming performed an ultrasound on each animal to measure body fat. This is a three-year study evaluating how body condition is related to pneumonia outbreaks.
The Jackson herd, which numbered 500 animals in the 1990s, has experienced two significant die-offs in recent years. In 2001, it was estimated that as many as 50% was lost due to a pneumonia outbreak and another estimated 30% lost again in 2011. Today it is estimated that the Jackson herd has climbed back to around 425 animals currently.
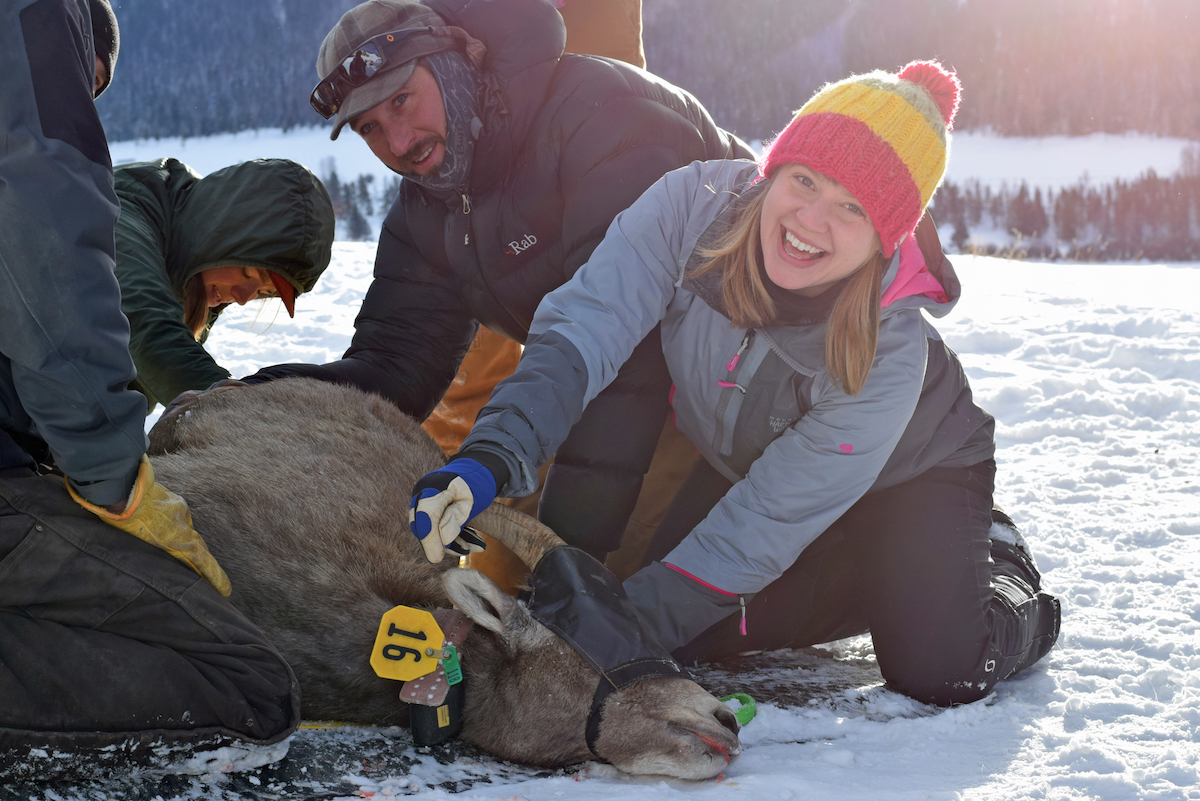

Kate Gersh and Greater Yellowstone Coalition wildlife program coordinator Chris Colligan assist the research team.
By monitoring individual female bighorn sheep (ewes) through time, researchers are assessing nutritional condition, pneumonia infection, and linking those data to reproductive performance, survival, and nutritional condition in subsequent seasons. At a minimum, they hope to begin to shed light on the complex interactions in the population dynamics of bighorn sheep and help identify possible management alternatives to reduce probability of pneumonia die-offs. For this specific research project, approximately 20 ewes have been collared. During the first three years of this project, biologists are expecting to recapture these same individual sheep each spring and fall to perform the same round of tests and evaluations. The team will go out again in March 2017, and attempt to catch more of their collared ewes to ascertain pregnancy and other health conditions.
JHWF staff is grateful to have been included in this project over the weekend and we thank the WGFD and Wyoming Cooperative Fish and Wildlife Research Unit for allowing us to see first-hand the efforts involved in conducting field research on bighorn sheep. We also thank all those involved for continuing to support wild sheep conservation efforts — you are doing excellent work!
View an image gallery of the work here.
References:
Bighorn Sheep Surveillance. (2016, March). Wyoming Game and Fish Department: Jackson Region Monthly Newsletter, 1. Retrieved December 13, 2016, from https://wgfd.wyo.gov/WGFD/media/content/PDF/Regional Offices/Jackson/2016_Mar_Jackson.pdf
Interview with Aly Courtemanch, Wildlife Biologist with Wyoming Game and Fish Department [Telephone interview]. (2016, December 13).
Koshmrl, M. (2015, March 25). Bighorns get their checkup. Jackson Hole News & Guide.
Nutritional dynamics and interactions with disease in bighorn sheep. (n.d.). Retrieved December 13, 2016, from http://wyocoopunit.org/projects/nutritional-dynamics-and-interactions-with-disease-in-bighorn-sheep.

by jhwildlife | Nov 21, 2016 | Blog, Wildlife Friendlier Landscapes
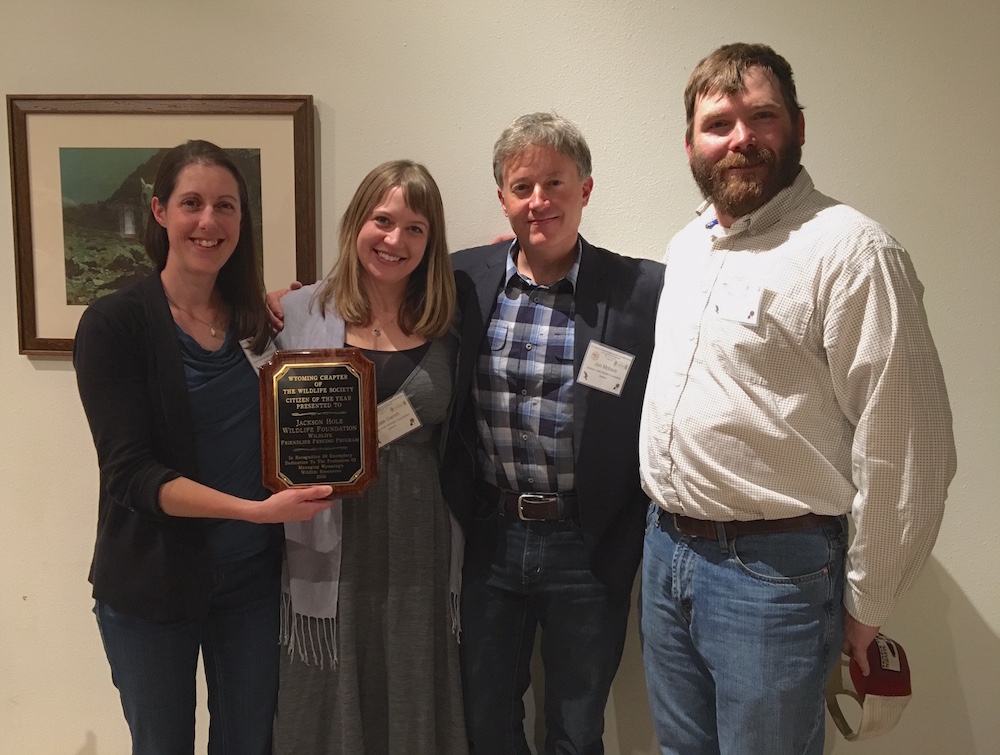

From left to right: JHWF Board President Aly Courtemanch, JHWF Associate Director Kate Gersh, JHWF Executive Director Jon Mobeck, Wyoming Chapter of The Wildlife Society Board Member Ben Wise
The Jackson Hole Wildlife Foundation received the Citizen of the Year Award for its Wildlife Friendlier Fencing Program on Thursday, November 17, at the Annual Meeting of the Wyoming Chapter of The Wildlife Society in Cody, Wyoming.
The Wyoming Chapter of The Wildlife Society Board Member Ben Wise announced the award at the closing evening banquet at the Buffalo Bill Center of the West. Wise introduced JHWF’s Executive Director Jon Mobeck to accept the award on behalf of the many hundreds of volunteers who, collectively, were recognized as Citizen of the Year. The Society typically gives the award to individuals who have made a significant contribution to wildlife management. Wise and other nominating agency partners from Wyoming Game & Fish and the Bridger-Teton National Forest saw an opportunity to celebrate the dedicated community that has formed around the Wildlife Friendlier Fencing program. The program’s impact exceeds the 183 miles of fence it has removed or modified over 20 years. It has also served to embody a community’s commitment to a land ethic that highly values landscape permeability.
In a brief acceptance comment, Mobeck alluded to Aldo Leopold’s oft-quoted mantra: “There are two things that interest me: the relation of people to each other, and the relation of people to land.” Mobeck concluded that one benefit of the Wildlife Friendlier Fencing program is that it advances meaningfully both of these relationships. JHWF believes that communities of people that come together for wildlife, especially throughout the rural West, may bridge social divides as we also clear barriers to wildlife movement. Since wildlife is a deeply shared interest in Wyoming – a Western passion – that connects people to each other, we believe that we can weave together the ethical fabric that allows a community to live compatibly with wildlife, while connecting individual communities to each other across a larger landscape. That ensures a bright future for wildlife in the Greater Yellowstone for generations to come.
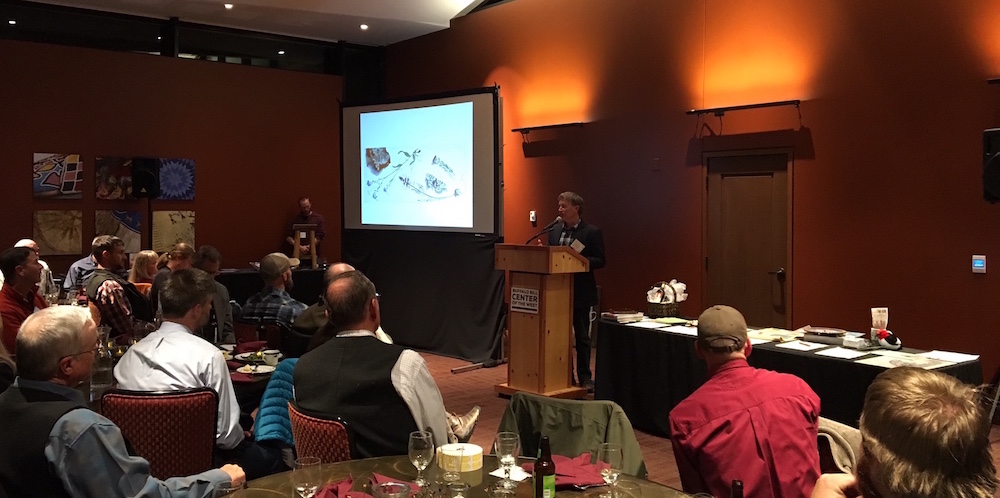

JHWF Executive Director Jon Mobeck accepts the Wyoming Chapter of The Wildlife Society’s Citizen of the Year award on behalf of program volunteers at the closing evening’s banquet dinner.
The conference in Cody, which brought together 150+ researchers, students and land managers for three days of talks, workshops, films, field trips and social gatherings, reflected this spirit. By promoting collaborative science and land management – and refreshingly linking art and science by inviting the gifted artist James Prosek to deliver the keynote talk at the banquet – the conference aims to build healthy and resilient landscapes for Wyoming’s wildlife and people.
On the opening evening of the conference, JHWF’s film “Free to Roam” was screened to a receptive and engaged audience. “Free to Roam” captures the essence of the Wildlife Friendlier Fencing program and many of the individuals who have been involved since its origin.
JHWF’s Board President Aly Courtemanch and Associate Director Kate Gersh also attended the conference, which enabled the organization to make many valuable connections to extend its reach, and learn from some of the best wildlife managers and advocates in the state.
The Wildlife Friendlier Fencing Program endures because of the relentless volunteer commitment of many individuals as well as the financial support of individual donors and many foundations and agencies over the years. Thank you to all who have made a contribution to this effort!
Read a short piece about the Award in the Jackson Hole News and Guide.


by jhwildlife | Oct 17, 2016 | Blog, Nature Mapping Jackson Hole
Registration is now open for the first ever Wyoming Citizen Science Conference! Hosted by the UW Biodiversity Institute, the conference will involve keynote and breakout sessions that guide program managers and citizen science participants (teachers, Scout leaders, community activists, etc.) to weigh in on what works well (and what doesn’t) in terms of having a successful, impactful citizen science program. The conference will be held in Lander, Wyoming, on December 1-2, 2016, and with an optional day on Saturday, December 3 to attend focused workshops.
We hope you can join us. The Jackson Hole Wildlife Foundation will be in attendance to represent Nature Mapping Jackson Hole – delivering two oral presentations and presenting two project posters in addition to, screening the film Far Afield. We’ll mainly be talking about lessons learned from the past eight years of Nature Mapping Jackson Hole, sharing our experiences and intending to learn much from others in attendance that will come from across the state. The organizers of this inaugural event hope to have a strong representation from active citizen scientists, not just those serving in professional capacities. Register today and come learn, share and be inspired!
Details on the conference agenda can be found here.





















